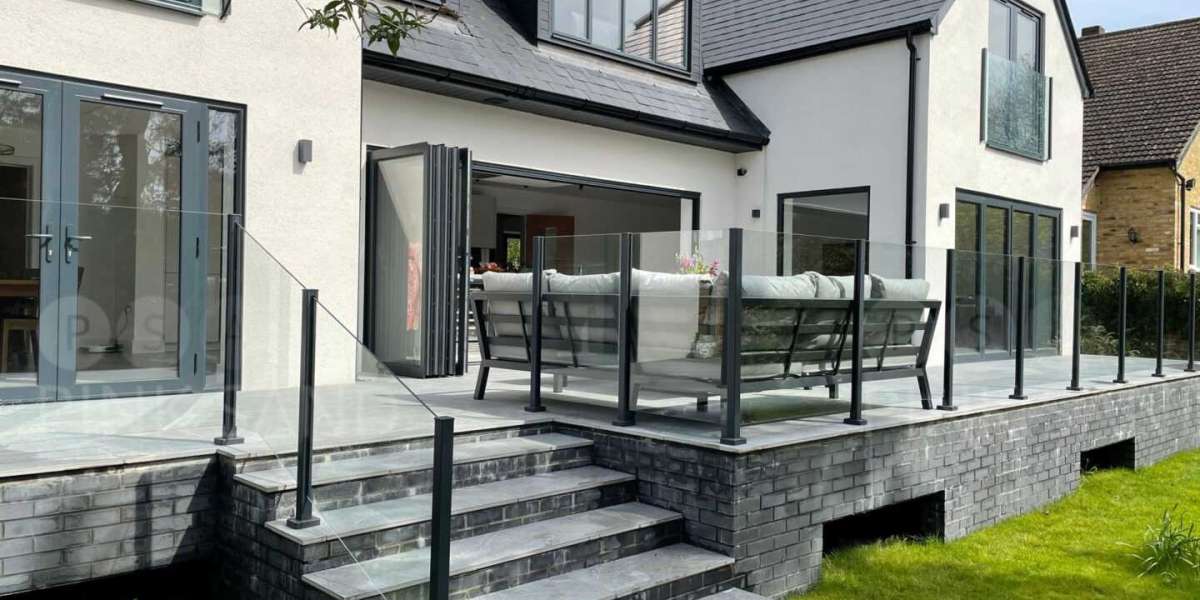
Glass balustrades have become increasingly popular in modern architecture and interior design due to their aesthetic appeal, safety features, and versatility. These transparent barriers, made primarily from tempered or laminated glass, are used in a variety of applications, including residential, commercial, and public spaces. This article explores the design considerations, safety regulations, benefits, and applications of glass balustrades, providing a comprehensive overview for architects, builders, and homeowners.
Design Considerations
When designing glass balustrades, several factors must be taken into account to ensure both functionality and aesthetics. One of the primary considerations is the type of glass used. Tempered glass, known for its strength and safety, is often preferred due to its ability to withstand impact and thermal stress. Laminated glass, which consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, offers additional safety benefits by preventing shattering.
Another important design aspect is the thickness of the glass. The thickness typically ranges from 10mm to 20mm, depending on the application and height of the balustrade. Thicker glass provides greater strength and stability, making it suitable for higher installations. Additionally, the design must consider the structural support system, which can include stainless steel posts, aluminum frames, or even frameless systems that rely on specialized hardware for mounting.
Aesthetic considerations also play a crucial role in the design of glass balustrades. The transparency of glass allows for unobstructed views, creating a sense of openness in spaces such as staircases, balconies, and terraces. Designers can choose from various finishes, including clear, frosted, or tinted glass, to achieve the desired look. Furthermore, the integration of lighting elements, such as LED strips, can enhance the visual appeal of glass balustrades, especially in low-light environments.
Safety Regulations
Safety is a paramount concern when it comes to glass balustrades, especially in public spaces and high-traffic areas. Various building codes and regulations govern the design and installation of glass balustrades to ensure they meet safety standards. In many jurisdictions, the International Building Code (IBC) provides guidelines on the minimum height, load requirements, and impact resistance of balustrades.
For instance, Trade Windows the IBC typically mandates that guardrails, including glass balustrades, must be at least 42 inches high for residential applications. Additionally, they must be capable of withstanding a minimum horizontal load, often specified as 200 pounds applied at any point. These regulations are designed to prevent falls and ensure the safety of individuals in proximity to the balustrade.
Moreover, the use of tempered or laminated glass is often required to enhance safety. In the event of breakage, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing the risk of injury. Laminated glass, on the other hand, remains intact even when broken, providing an additional layer of protection.
Benefits of Glass Balustrades
The use of glass balustrades offers numerous benefits, making them an attractive option for both residential and commercial applications. One of the most significant advantages is their ability to create a sense of space and light. Unlike traditional materials such as wood or metal, glass allows natural light to flow freely, enhancing the overall ambiance of a space.
In addition to their aesthetic appeal, glass balustrades are also low-maintenance. Unlike wood, which requires regular staining or painting, glass can be easily cleaned with standard glass cleaners. This durability makes glass balustrades an excellent choice for outdoor applications, where exposure to the elements can lead to deterioration of other materials.
Another benefit is the flexibility of design. Glass balustrades can be customized to fit a variety of architectural styles, from contemporary to traditional. They can be integrated into various settings, including staircases, balconies, terraces, and swimming pools, providing a seamless transition between indoor and outdoor spaces.
Applications of Glass Balustrades
Glass balustrades are utilized in a wide range of applications, reflecting their versatility and adaptability. In residential settings, they are commonly used for staircases, balconies, and pool fences. Their transparent nature enhances the visual appeal of these areas while ensuring safety for family members and guests.
In commercial spaces, glass balustrades are often employed in office buildings, shopping malls, and hotels. They serve as both functional barriers and design elements, contributing to the overall aesthetic of the space. For instance, in a hotel lobby, a glass balustrade can create an open and inviting atmosphere while providing safety for guests.
Public spaces, such as parks, museums, and transportation hubs, also benefit from the use of glass balustrades. They can be used to create safe viewing areas, protect pedestrians, and enhance the overall design of the environment. In these applications, the transparency of glass allows for unobstructed views of the surroundings, promoting engagement with the space.
Conclusion
Glass balustrades represent a harmonious blend of safety, aesthetics, and functionality. Their ability to enhance the visual appeal of a space while providing essential safety features makes them a popular choice in modern architecture. As design trends continue to evolve, the demand for glass balustrades is likely to grow, driven by their versatility and adaptability in various applications. By understanding the design considerations, safety regulations, and benefits associated with glass balustrades, architects, builders, and homeowners can make informed decisions that contribute to the creation of beautiful and safe environments.